Algoritmos de ordenamiento con simulaciones e implementación en varios lenguajes c, python, c++
Алгоритмы сортировки с имитацией и реализацией на разных языках c, python, c ++
Sorting algorithms with simulations and implementation in various languages c, python, c ++
Algoritmos de ordenamiento con simulaciones e implementación en varios lenguajes
http://lwh.free.fr/pages/algo/tri/tri_es.htm
Algoritmos de ordenamiento con simulaciones e imlementación en c++
https://www.hackerearth.com/practice/algorithms/sorting/insertion-sort/tutorial/
Sorting
Algoritmos de ordenamiento
Los algoritmos de ordenamiento nos permite, como su nombre lo dice, ordenar información de una manera especial basándonos en un criterio de ordenamiento.
En la computación el ordenamiento de datos cumple un rol muy importante, ya sea como un fin en sí o como parte de otros procedimientos más complejos. Se han desarrollado muchas técnicas en este ámbito, cada una con características específicas, y con ventajas y desventajas sobre las demás.
Para que os hagáis una idea de la dificultad del problema, propongo el siguiente mini juego. Se trata de unos barriles ordenar (entre 3 y 10) con el fin de aumentar de peso. El peso de cada barril fue asignado al azar. Utilice la opción "arrastrar y soltar" para mover los barriles.
Tienes una escala no calibrada que le permite comparar el peso de barriles y estantes que pueden servir para el almacenamiento intermedio. Estos son exactamente los mismos elementos que los que están disponibles a un ordenador: una función de comparación y áreas de almacenamiento. El objetivo es, obviamente, de ordenar los barriles con los menos comparaciones e intercambios posibles.
Las siguientes páginas presentan los principales métodos de ordenamiento :
- Searching
- Sorting
- Greedy Algorithms
- Graphs
- String Algorithms
- Dynamic Programming
Insertion Sort
- TUTORIAL
- PROBLEMS
- VISUALIZERBETA
Insertion sort is based on the idea that one element from the input elements is consumed in each iteration to find its correct position i.e, the position to which it belongs in a sorted array.
It iterates the input elements by growing the sorted array at each iteration. It compares the current element with the largest value in the sorted array. If the current element is greater, then it leaves the element in its place and moves on to the next element else it finds its correct position in the sorted array and moves it to that position. This is done by shifting all the elements, which are larger than the current element, in the sorted array to one position ahead
Implementation
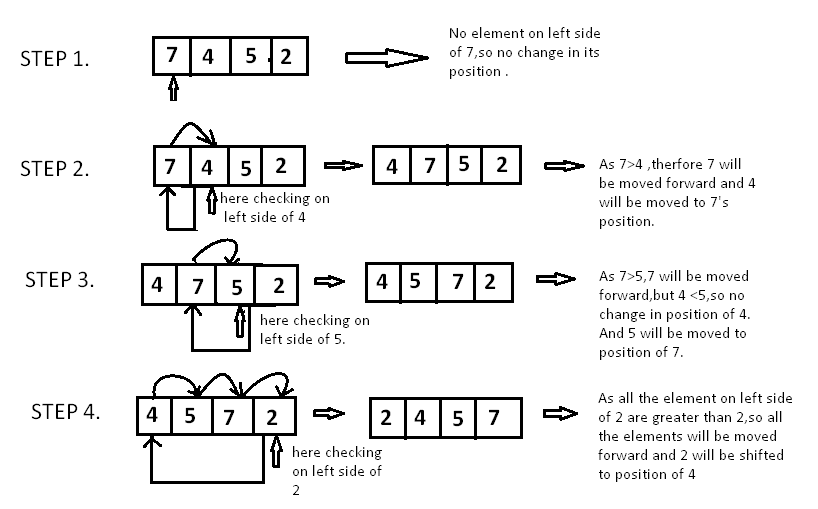
Since is the first element has no other element to be compared with, it remains at its position. Now when on moving towards , is the largest element in the sorted list and greater than . So, move to its correct position i.e. before . Similarly with , as (largest element in the sorted list) is greater than , we will move to its correct position. Finally for , all the elements on the left side of (sorted list) are moved one position forward as all are greater than and then is placed in the first position. Finally, the given array will result in a sorted array.
Time Complexity:
In worst case,each element is compared with all the other elements in the sorted array. For elements, there will be comparisons. Therefore, the time complexity is
It iterates the input elements by growing the sorted array at each iteration. It compares the current element with the largest value in the sorted array. If the current element is greater, then it leaves the element in its place and moves on to the next element else it finds its correct position in the sorted array and moves it to that position. This is done by shifting all the elements, which are larger than the current element, in the sorted array to one position ahead
Implementation
void insertion_sort ( int A[ ] , int n)
{
for( int i = 0 ;i < n ; i++ ) {
/*storing current element whose left side is checked for its
correct position .*/
int temp = A[ i ];
int j = i;
/* check whether the adjacent element in left side is greater or
less than the current element. */
while( j > 0 && temp < A[ j -1]) {
// moving the left side element to one position forward.
A[ j ] = A[ j-1];
j= j - 1;
}
// moving current element to its correct position.
A[ j ] = temp;
}
}
Since is the first element has no other element to be compared with, it remains at its position. Now when on moving towards , is the largest element in the sorted list and greater than . So, move to its correct position i.e. before . Similarly with , as (largest element in the sorted list) is greater than , we will move to its correct position. Finally for , all the elements on the left side of (sorted list) are moved one position forward as all are greater than and then is placed in the first position. Finally, the given array will result in a sorted array.
Time Complexity:
In worst case,each element is compared with all the other elements in the sorted array. For elements, there will be comparisons. Therefore, the time complexity is
Contributed by: Anand Jaisingh
well explained keep up the good work also check mine on
ResponderEliminarraspberry pinout
and
Serial communication