https://www.javatpoint.com/bash-arithmetic-operators
Performing Arithmetic Operations in Bash
There are many options to perform arithmetic operations on the bash shell. Some of the options are given below that we can adopt to perform arithmetic operations:
Double Parentheses
Double parentheses is the easiest mechanism to perform basic arithmetic operations in the Bash shell. We can use this method by using double brackets with or without a leading $.
Syntax
We can apply four different ways to achieve the required objectives. Look at the methods given below to understand how the double parentheses mechanism can be used (Assuming that we want to add the numbers 10 and 3) :
Method 1
Method 2
Method 3
Method 4
All of these methods will provide the same output as:
Sum = 13
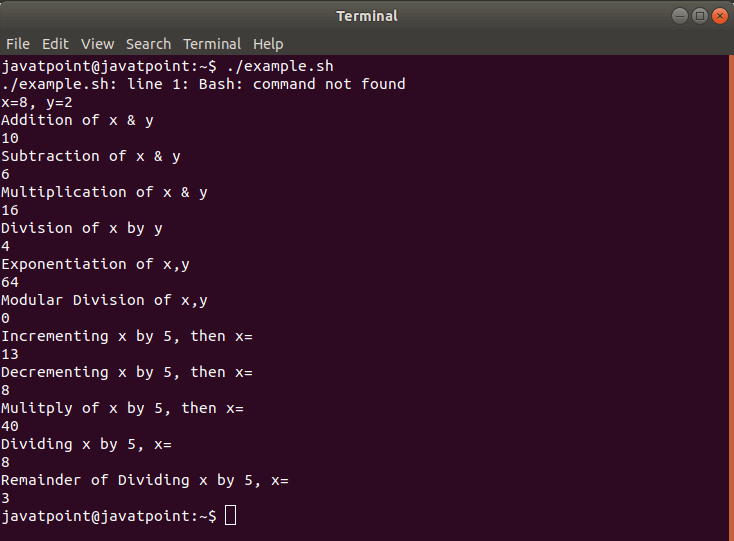
Following is an example demonstrating the use of double parentheses for arithmetic operations in a Bash shell script:
Bash Script
Output
Let Construction
Let is a built-in command of Bash that allows us to perform arithmetic operations. It follows the basic format:
Syntax
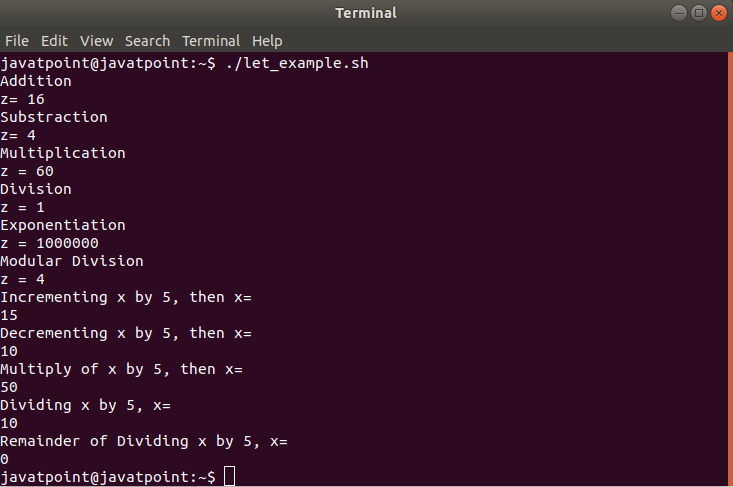
An example is given below explaining how to use let command in a Bash script:
Bash script
Output
Backticks
In bash scripting, an arithmetic expansion can also be performed using backticks and expr (known as all-purpose expression evaluator). The `expr` is similar to 'let,' but it does not save the result to a variable. It directly prints the result. Unlike let, we don't need to enclose the expression within the quotes. We are required to use spaces between the items of the expression. It is important to note that we should use 'expr` within command substitution to save the output to a variable.
We can also use `expr` without 'backticks'.
Syntax
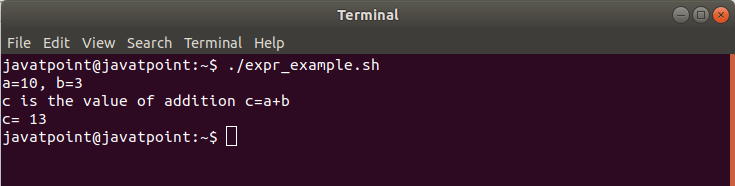
An example is given below explaining how to use backticks and expr in a Bash script:
Bash Script Program
Output
Conclusion
In this topic, we discussed how to use arithmetic operators to perform arithmetic operations.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario