Range Object
Range Examples | Cells | Declare a Range Object | Select | Rows | Columns | Copy/Paste | Clear | Count
The Range object, which is the representation of a cell (or cells) on your worksheet, is the most important object of Excel VBA.
This chapter gives an overview of the properties and methods of the
Range object. Properties are something which an object has (they
describe the object), while methods do something (they perform an action
with an object).Range Examples
Place a command button on your worksheet and add the following code line:
Range("B3").Value = 2
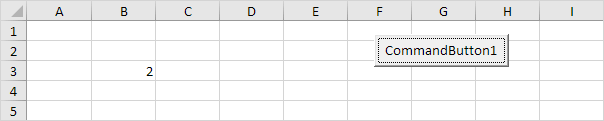
Code:
Range("A1:A4").Value = 5
Result: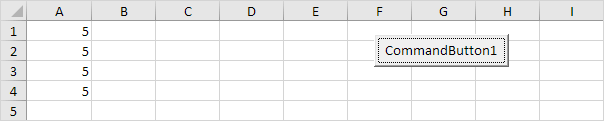
Code:
Range("A1:A2,B3:C4").Value = 10
Result: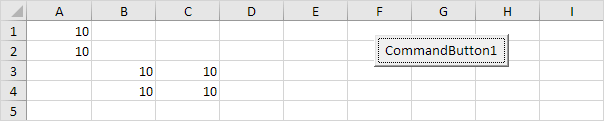
Note: to refer to a named range in your Excel VBA code, use a code line like this:
Range("Prices").Value = 15
Cells
Instead of Range, you can also use Cells. Using Cells is particularly useful when you want to loop through ranges.Code:
Cells(3, 2).Value = 2
Result: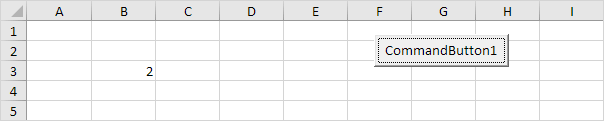
Explanation: Excel VBA enters the value 2 into the cell at the intersection of row 3 and column 2.
Code:
Range(Cells(1, 1), Cells(4, 1)).Value = 5
Result: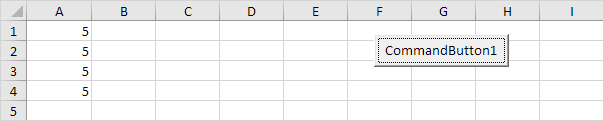
Declare a Range Object
You can declare a Range object by using the keywords Dim and Set.Code:
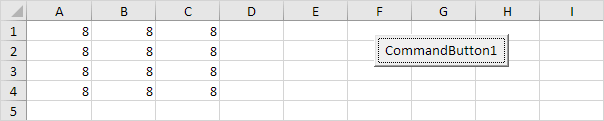
Dim example As Range
Set example = Range("A1:C4")
example.Value = 8
Result:Set example = Range("A1:C4")
example.Value = 8
Select
An important method of the Range object is the Select method. The Select method simply selects a range.Code:
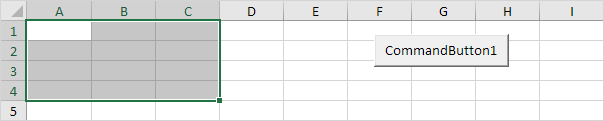
Dim example As Range
Set example = Range("A1:C4")
example.Select
Result:Set example = Range("A1:C4")
example.Select
Rows
The Rows property gives access to a specific row of a range.Code:
Dim example As Range
Set example = Range("A1:C4")
example.Rows(3).Select
Result:Set example = Range("A1:C4")
example.Rows(3).Select
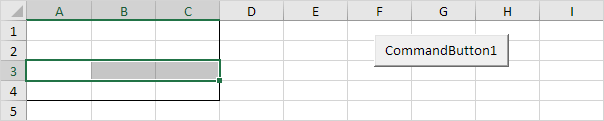
Note: border for illustration only.
Columns
The Columns property gives access to a specific column of a range.Code:
Dim example As Range
Set example = Range("A1:C4")
example.Columns(2).Select
Result:Set example = Range("A1:C4")
example.Columns(2).Select
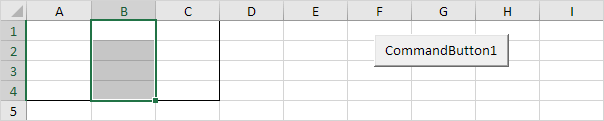
Note: border for illustration only.
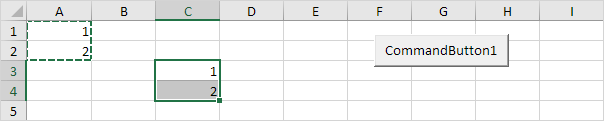
Copy/Paste
The Copy and Paste method are used to copy a range and to paste it somewhere else on the worksheet.Code:
Range("A1:A2").Select
Selection.Copy
Range("C3").Select
ActiveSheet.Paste
Result:Selection.Copy
Range("C3").Select
ActiveSheet.Paste
Although this is allowed in Excel VBA, it is much better to use the code line below which does exactly the same.
Range("C3:C4").Value = Range("A1:A2").Value
Clear
To clear the content of an Excel range, you can use the ClearContents method.
Range("A1").ClearContents
or simply use:
Range("A1").Value = ""
Note: use the Clear method to clear the content and format of a range. Use the ClearFormats method to clear the format only.Count
With the Count property, you can count the number of cells, rows and columns of a range.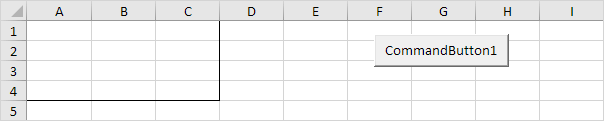
Note: border for illustration only.
Code:
Dim example As Range
Set example = Range("A1:C4")
MsgBox example.Count
Result:Set example = Range("A1:C4")
MsgBox example.Count
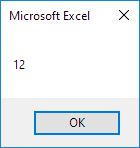
Code:
Dim example As Range
Set example = Range("A1:C4")
MsgBox example.Rows.Count
Result:Set example = Range("A1:C4")
MsgBox example.Rows.Count
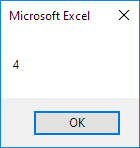
Note: in a similar way, you can count the number of columns of a range.
No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario